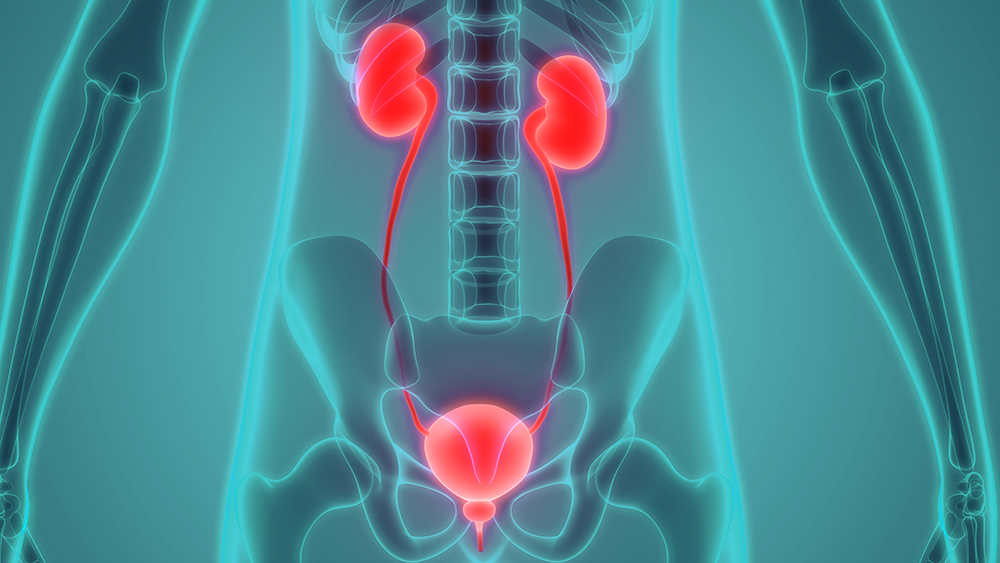
A urinary tract infection is an inflammation (infection) of the mucous membrane located on the inside of the urinary tract. Urinary tracts include all structures through which urine leaves the body: the renal pelvis, the ureters, the bladder, and the urethra.
The infection occurs when bacteria, usually originating from the gastrointestinal tract, attach themselves to the opening of the urethra. If they get the chance to move into the urethra, they start to multiply.
Bladder Infection
When an infection is limited to the urethra, we call it ‘urethritis’. Sometimes, however, bacteria don’t stop their unwanted journey through the body and move to the bladder. This results in a bladder infection (cystitis).
The E. coli bacterium, a common intestinal bacterium, is the main cause.
Women are at a higher risk of urinary tract infections and bladder infections
They occur much more frequently in women than in men. Women therefore have an increased risk that also increases with age.
Due to the shorter urethra (urinary tract), bacteria can more easily enter the urethra. This can also happen during intercourse. That’s why women sometimes get a bladder infection after sexual activity.
After using the toilet, incorrect wiping (from back to front) is the second largest cause of infections.
Wearing tight and poorly breathable clothing and underwear also increases the chance of a bladder infection.
Symptoms of bladder infection:
- Needing to urinate more frequently
- Feeling the urge to urinate, even when it’s a false alarm
- Passing small amounts of urine frequently
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Pain when urinating
- The urine may be cloudy or contain blood
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- No fever but slightly elevated temperature
- Recurrent (recurring) bladder infection or urinary tract infection
- We speak of a recurring or recurrent urinary tract infection / bladder infection if it occurs 3 times or more in one year.
Kidney Infection
Sometimes a urinary tract infection can develop into a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). This usually occurs as a result of a bladder infection. From the bladder, the bacteria travel via the ureters to the kidneys. They enter the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis is a cavity in the kidney. There, the bacteria cause inflammation in the kidney tissue. It’s also possible for the bacteria to enter the kidney via the bloodstream.
The symptoms of a kidney infection (Pyelonephritis) are the same as a bladder infection. But the patient often also has high fever, chills, and pain in the side or back, nausea and vomiting. These symptoms are usually preceded by a bladder infection. Kidney infection usually occurs in only one kidney.
How to prevent a bladder infection or urinary tract infection?
These tips can help:
- Drink enough, preferably 1.5 to 2 liters per day
- Don’t unnecessarily postpone urinating, go to the toilet when you feel the urge
- Empty the bladder completely (this may take a while)
- Urinate immediately after sexual intercourse. Bacteria that have entered the urethra during intercourse are immediately flushed out